There is no doubt that technological advancement has greatly improved the aspect of product development. Rapid prototyping and 3D printing are just some of the results. Many people have embraced these two methods of product development.
Technically, both 3D printing and Rapid prototyping product development methods that are used in additive manufacturing. Most people tend to assume that the two are the same thing.
Is 3D printing the same as rapid prototyping?
While there are glaring similarities between rapid prototyping 3D printing, these two methods of manufacturing are completely different. In this blog post, we are going to distinguish rapid prototyping vs 3D printing.
Contents
Understanding Additive Manufacturing
Before we even differentiate between 3D printing and rapid prototyping, let us have a first look at their basis. Both of them are derived from additive manufacturing.
But, what is additive manufacturing?
As the name suggests, additive manufacturing entails building a product by adding materials layer by layer. The addition is done repeatably and These layers end up forming one single product.
Additive manufacturing is the opposite of subtractive manufacturing whereby products are created by cutting the materials bit by bit through a machining process.
Defining 3D Printing and Rapid Prototyping
What is 3D Printing?
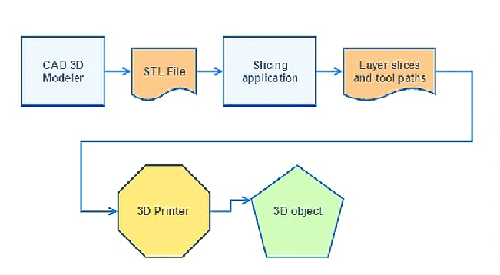
3D printing is an elaborate manufacturing process that entails taking the 3D model and turning it into a physical object. The digital file is transformed into a 3D object.
Creating a 3D printed object is achieved through the additive manufacturing method. Successive layers of the material are laid until the final object comes into life. Each layer is visible through the cross-section of the object.
Through 3D printing, complex objects and products can be created from very few materials. The product can then be subjected to post-processing methods such as painting and polishing.
What is Rapid Prototyping?
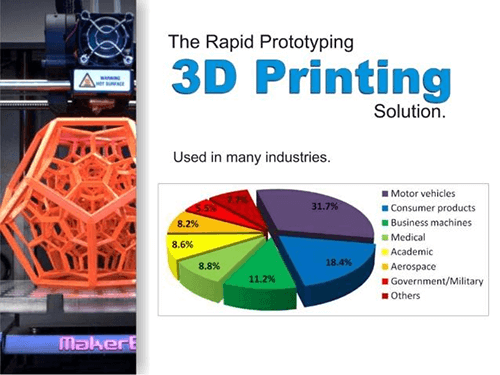
Rapid prototyping (RP) is a type of additive manufacturing technique that is designed to create models faster than in normal manufacturing techniques. The process is done using computer-aided design data (CAD)
Rapid prototyping process is usually completed by different methods of additive manufacturing such as 3D printing.
Through rapid prototyping, three-dimensional models of a product or part of the product are visually generated. Some aspects of the generated product such as efficiency and effectiveness can be tested before they are manufactured in large scale
The Process: 3D Printing vs Rapid Prototyping
How does 3D printing work?
Everything starts with the creation of the 3D model. The models are usually created by experienced 3D designers. Alternatively, you can download ready-made models on the internet.
There is curated software that is used for creating the models.
Once you have the model, the next step is to prepare the file for the 3D printer in a process known as slicing.
Slicing entails dividing the 3D models into several layers. The process is done using a special slicing software.
Once the 3D file has been sliced, each slice is fed into a 3D printer. The printing then commences through the additive manufacturing process.
How does rapid prototyping work?
There are several manufacturing techniques that are used for implementing rapid prototyping. Most of these techniques follow the rules of the additive manufacturing process.
Apart from the additive method, rapid prototyping also encompasses other techniques such as compressive manufacturing. This is where a semi-solid or liquid material is forced into the shape of a particular product.
Other rapid prototyping techniques include subtractive manufacturing, casting, and 3D printing.
From this difference, you can tell that 3D printing involves a single manufacturing process that is followed sequentially. On the other hand, rapid prototyping has many techniques that are aimed at cutting down the time taken to manufacture products.
Advantages: 3D Printing vs Rapid Prototyping
When comparing these two types of manufacturing, it is sensible that we look at the benefits of each method.
Benefits of 3D Printing
-Faster production process
-High-quality products
-Easy to test the products
-Cost-effective method of manufacturing
-It gives freedom for one to be more creative in terms of coming up with unique designs.
-Provides unlimited geometry, shapes, and dimensions
-Minimum wastage of the materials
-Allows usage of different types of materials.
-Reduction of risks during the manufacturing process.
-Easy to monitor and follow the procedure
Benefits of Rapid Prototyping
-Speed up the production and manufacturing process. This is the primary goal of rapid prototyping.
-Cost-effective. The techniques for this method of manufacturing are cheap. You will save money through 3D and CNC machining.
-Allows one to test and explore different designs and d geometries of a product.
-Helps to avoid or mitigate risks that come with the manufacturing process
-You can test the materials before using them to manufacture products.
From this comparison, it is clear that the benefits of 3D printing and rapid prototyping are almost similar in some way.
Price: 3D Printing vs Rapid Prototyping
Which one is expensive between 3D printing and rapid prototyping?
There is a significant difference in price between these two types of manufacturing or product development. The price factor includes expenses such as labor depreciation of the materials and maintenance.
Rapid prototyping is always viewed to be costlier than 3D printing. First, the cost of buying rapid prototyping systems can be as high as $75,000. Although this may not seem to be a big issue, there are recurring costs that you will still have to incur.
The cost of maintaining some rapid prototyping systems can be as high as $10,000 per year.
On the other hand, 3D printing also attracts some costs such as maintaining the 3D printer. However, this cost will still be much less than what you will need for maintaining the equipment for rapid prototyping.
From a financial perspective, it is vital that you do your homework before choosing either RP or 3D printing. Find out all the issues starting from the price of the systems to the cost of maintaining.
If you are outsourcing the services, you should also request the quotations from the 3D printing and rapid prototyping companies in China.
The complexity of the Method: 3D Printing vs Rapid Prototyping
Which one is easy and which one is complex between 3D printing vs rapid prototyping?
Although both the methods of manufacturing are quite technical, their degrees of complexity varies. 3D printing is not as complicated as rapid prototyping.
The level of training that is required for 3D printing is less than that of rapid prototyping. However, this training will depend on the 3D machines to be used and parts to be produced.
Adjusting the parameters on the rapid prototyping can be quite a difficult mission to accomplish. The learning curve for rapid prototyping is relatively longer than that of 3D printing.
Do you know that it is very possible to create parts straight from the design stage thanks to the 3D printing? Also, the fact that 3D printing is less means that the time taken for the production process can also be reduced.
However, regardless of their complexities, both 3D printing and rapid prototyping should be handled by experts. This will ensure that the end product meets the desired standards.
Materials Used: 3D Printing vs Rapid Prototyping
Which materials are used in 3D printing and which ones are for rapid prototyping? Which one can accommodate more materials?
Since rapid prototyping encompasses many manufacturing techniques, it is expected that the method can be used on a wide range of materials. It can be used for both hard and soft material.
On the other hand, 3D printing is slightly limited as compared to rapid prototyping. It is best suited for PVC and plastics.
However, the advancement of technology is expanding the capability of 3D printing. Now it can be used for producing more materials such as ceramics among others.
When it comes to choosing the materials, ensure that you consult with the 3D printing company or rapid prototyping service provider.
Accuracy: 3D Printing vs Rapid Prototyping
Regardless of the product that you are manufacturing, the issue o accuracy will always remain paramount. Which one is more accurate between 3D printing vs rapid prototyping?
In terms of accuracy, rapid prototyping is capable of producing more accurate finishes than 3D printing. This is despite the fact that both the two methods rely on the underlying geometry
The reliance on part-accuracy technology is attributed to the accuracy of the rapid prototyping.
You should also note that the accuracy of the 3D printers can be limited to the sizes of the products. They may not be very accurate when it comes to producing large objects.
However, the advancement of technology has resulted in more accurate and efficient 3D printers.
Conclusion
Despite the differences, both 3D printing and rapid prototyping can help you to achieve your business goals. They will give you opportunities to produce a wide range of products.
The secret of succeeding in either method of production is choosing the right company. This is why we at Roche Industry provide reliable 3D printing and Rapid Prototyping services in China. Contact us for more about these two additive manufacturing methods.
Rocheindustry specializes in high quality rapid prototyping, rapid low-volume manufacturing and high-volume production. The services of rapid prototype we providing are professional Engineering, CNC Machining including CNC Milling and Turning, Sheet Metal Fabrication or Sheet Metal Prototyping, Die casting, metal stamping, Vacuum Casting, 3D printing, SLA, Plastic and Aluminum Extrusion Prototyping, Rapid Tooling, Rapid Injection Moulding, Surface Treatment finish services and other rapid prototyping China services please contact us now.